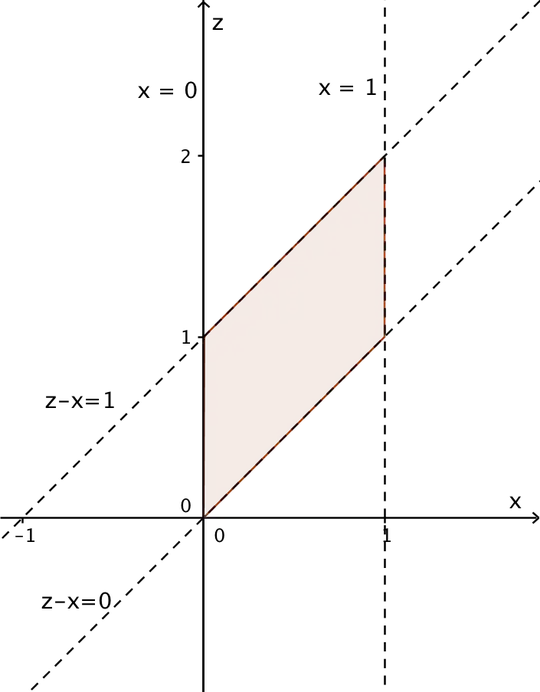
I provide a method here by using bivariate transformation. Let $X \sim Uniform(0,1)$ and $Y \sim Uniform(0,1)$. $X$ and $Y$ are independent. We want to know the density of $X+Y$.
Since X and Y are independent, then their joint distribution is
\begin{equation}
\begin{split}
f_{X,Y}(x,y)&=f_X(x) f_Y(y) \\
&= \begin{cases}
1 &\text{if $0<x<1, 0<y<1$}\\
0 &\text{otherwise}
\end{cases}
\end{split}
\end{equation}
Now let $U=X+Y, V=X$. Thus $X=V=h_1(u,v), Y=U-V=h_2(u,v)$. It is easy to compute that $|J|=1$
Thus,
\begin{equation}
\begin{split}
f_{U,V}(u,v) &= f_{X,Y}(h_1(u,v),h_2(u,v)) |J| \\
&= \begin{cases}
1 &\text{if $(u,v) \in \mathcal{B} $}\\
0 &\text{otherwise}
\end{cases}
\end{split}
\end{equation}
where $\mathcal{A}=\{(x,y):f_{X,Y}(x,y) >0\} $ and $\mathcal{B}=\{(u,v):u=g_1(x,y), v=g_2(x,y) \text{ for some $(x,y) \in \mathcal{A}$}\}$
We need to know what $\mathcal{B}$ is. Since $0<x<1,o<y<1$, this is equivalent to $0<v<1, 0<u-v<1$, also equivalent to $0<v<1, v<u<v+1$. Thus $\mathcal{B} = \{ (u,v): 0<v<1, v<u<v+1$ }
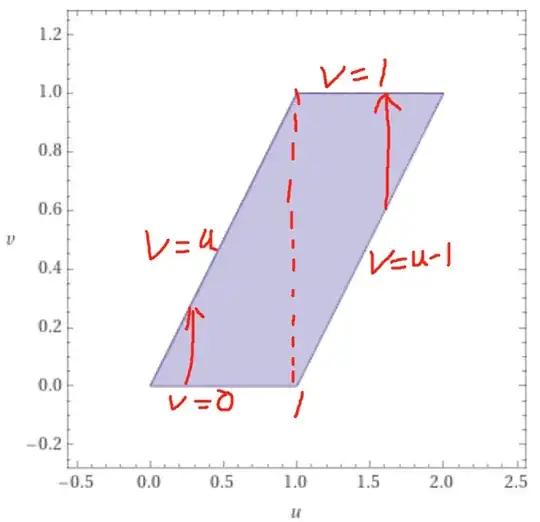
Then $f_U(u) = \int_{-\infty}^\infty f_{U,V}(u,v) dv=\int_\mathcal{B} f_{U,V}(u,v) dv=\int_\mathcal{B} 1 dv $
Notice that $0<v<1, v<u<v+1$ implies $0<u<2$. When $0<u<1$, v varies from 0 and u. Thus $\int_\mathcal{B} 1 dv = \int_0^u 1dv=u$. When $1<u<2$, v varies from $u-1$ and 1. Thus $\int_\mathcal{B} 1 dv = \int_{u-1}^1 1dv=2-u$. Together the result holds.