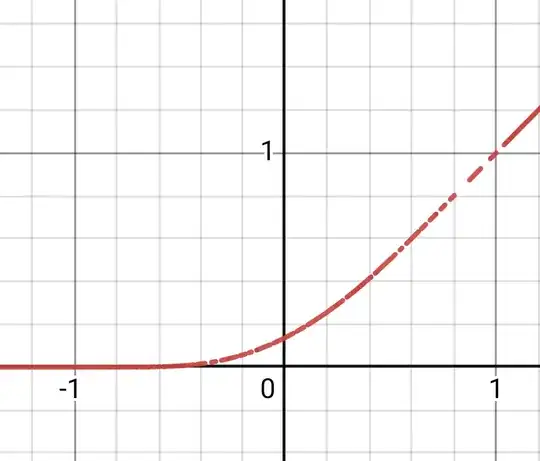
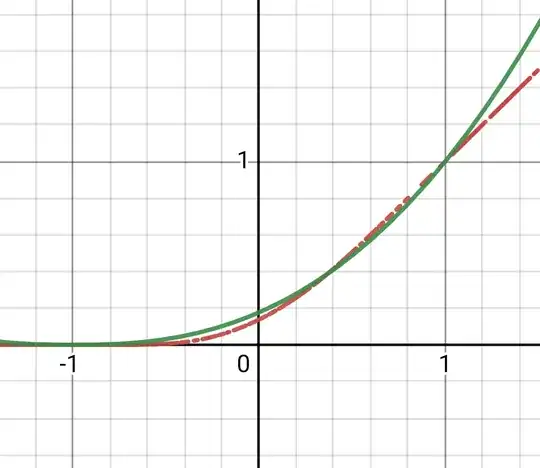
Though not quite a standard power series, one can derive the series representation
$$g(x)=\int\limits_{-1}^x \frac{1}{e^{\frac{4 u}{u^2-1}}+1} \, du= \frac{x+1}{2}+\underset{N\to\infty}{\text{lim}}\left(\sum\limits_{n=1}^N \frac{a_n}{2 n} \left(x^{2 n}-1\right)\right),\quad -1<x<1\tag{1}$$
from the Maclaurin series
$$f(u)=\frac{1}{e^{\frac{4 u}{u^2-1}}+1}=\frac{1}{2}+\underset{N\to\infty}{\text{lim}}\left(\sum_{n=1}^N a_n u^{2 n-1}\right),\quad -1<u<1 \tag{2}$$
where $a_n=\frac{f^{(2n-1)}(0)}{(2 n-1)!}$ via term-wise integration, i.e. $\int\limits_{-1}^x \frac{1}{2} \, du=\frac{x+1}{2}$ and $\int\limits_{-1}^x a_n u^{2n-1} \, du=\frac{a_n}{2 n} \left(x^{2 n}-1\right)$.
The first few terms of the series for $f(u)$ are
$$f(u)=\frac{1}{2}+u-\frac{u^3}{3}-\frac{13 u^5}{15}+\frac{67 u^7}{315}+\frac{3083 u^9}{2835}...\tag{3}$$
and the first few terms of the series for $g(x)$ are
$$g(x)=\frac{x+1}{2}+\frac{x^2-1}{2}-\frac{x^4-1}{12}-\frac{13 \left(x^6-1\right)}{90}+\frac{67 \left(x^8-1\right)}{2520}+\frac{3083 \left(x^{10}-1\right)}{28350}..\tag{4}.$$
Figure (1) below illustrates $f(u)=\frac{1}{e^{\frac{4 u}{u^2-1}}+1}$ in blue and the Maclaurin Series for $f(x)$ in orange where the series defined in formula (2) above is evaluated at $N=100$.
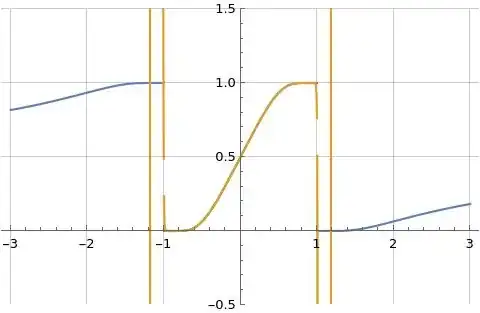
Figure (1): Illustration of $f(u)=\frac{1}{e^{\frac{4 u}{u^2-1}}+1}$ (blue) and associated Maclaurin series (orange)
Figure (2) below illustrates $g(x)=\int\limits_{-1}^x \frac{1}{e^{\frac{4 u}{u^2-1}}+1} \, du$ in blue and the series for $g(x)$ in orange where the integral in formula (1) above is evaluated using numerical integration (via Mathematica's NIntegrate function) and the series defined in formula (1) above is evaluated at $N=100$.

Figure (2): Illustration of $g(x)=\int\limits_{-1}^x \frac{1}{e^{\frac{4 u}{u^2-1}}+1} \, du$ (blue) and associated series (orange)
One can also derive the Maclaurin series
$$g(x)=\int\limits_{-1}^x \frac{1}{e^{\frac{4 u}{u^2-1}}+1} \, du=b+\frac{x}{2}+\underset{N\to\infty}{\text{lim}}\left(\sum\limits_{n=1}^N \frac{a_n}{2 n}\, x^{2 n}\right),\quad -1<x<1\tag{5}$$
where
$$b=\int\limits_{-1}^0 \frac{1}{e^{\frac{4 u}{u^2-1}}+1} \, du\approx 0.137775\tag{6}$$
and $a_n$ is the same as in formulas (1) and (2) above.
The first few terms of the Maclaurin series for $g(x)$ defined in formula (5) above are
$$g(x)=b+\frac{x}{2}+\frac{x^2}{2}-\frac{x^4}{12}-\frac{13 x^6}{90}+\frac{67 x^8}{2520}+\frac{3083 x^{10}}{28350}...\tag{7}$$
Figure (3) below illustrates $g(x)=\int\limits_{-1}^x \frac{1}{e^{\frac{4 u}{u^2-1}}+1} \, du$ in blue and the Maclaurin series for $g(x)$ defined in formula (5) above in orange where the integral in formula (5) above is evaluated using numerical integration and the Maclaurin series defined in formula (5) above is evaluated at $N=100$.

Figure (3): Illustration of $g(x)=\int\limits_{-1}^x \frac{1}{e^{\frac{4 u}{u^2-1}}+1} \, du$ (blue) and formula (5) Maclaurin series (orange)