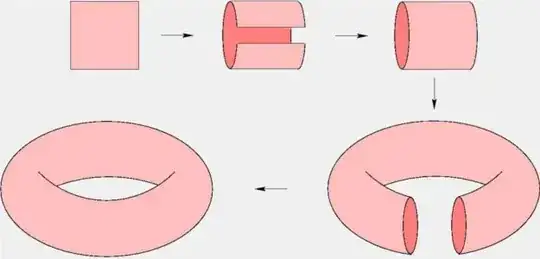
We know that torus can be obtained from a square by joining the opposite sides.
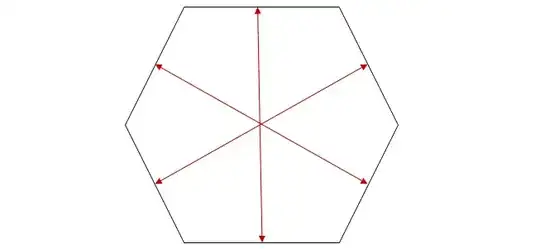
Can we do the same thing with a hexagon?
If it's not possible to 'fold' hexagon in 3D Euclidean space, may be it's possible in highter dimensions?
Of course, like in the example with a square, stretching is allowed.
I intentionaly don't use the correct topology terms, since I don't know topology. I probably should've used terms such as manifold and homeomorphism.
I hope the question is clear enough in layman terms.
Related question: What are all topological spaces obtained by gluing the edges of a triangle?
Edit
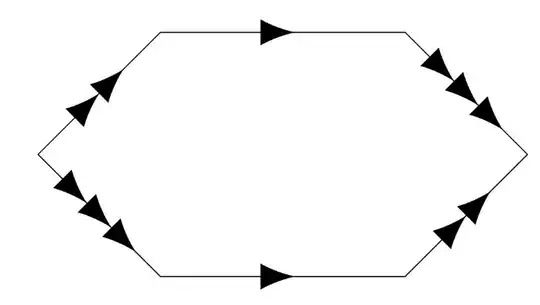
A useful link from Fredrik Meyer which probably answers the question. And the image from the link which should help with orienation:
we see that the surface is the torus.
Says the link. If it's true, can we show how folding a hexagon results in a torus?