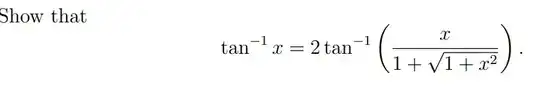
It quite confuses me. Where do I start?
Please help.
HINT:
Putting $\tan^{-1}x=2\theta$
$\displaystyle\implies (i)\tan2\theta= x$ and $\displaystyle(ii)-\frac\pi2\le 2\theta\le\frac\pi2$ based on the definition of principal value of inverse tangent ratio
$\displaystyle\implies \frac x{1+\sqrt{1+x^2}}=\frac{\tan2\theta}{1+\sqrt{1+\tan^22\theta}}$
$\displaystyle=\frac{\tan2\theta}{1+\sec2\theta}$ as $\displaystyle\sec2\theta=\frac1{\cos2\theta}>0$ in $\displaystyle\left[-\frac\pi2,\frac\pi2\right]$
$\displaystyle=\frac{\sin2\theta}{1+\cos2\theta}=\frac{2\sin\theta\cos\theta}{2\cos^2\theta}=\tan\theta$ as $\cos\theta\ne0$ as $\displaystyle-\frac\pi4\le\theta\le\frac\pi4$
hint:
i) Apply $\tan x $ to both sides.
ii) use the formula for $\tan( a+b) $ on the right hand side and simplify.
In fact, we can use this to find,
$$2\tan^{-1}x=\begin{cases} \tan^{-1}\frac{2x}{1-x^2} &\mbox{if } x^2<1\iff -1\le x\le1 \\\pi+ \tan^{-1}\frac{2x}{1-x^2} & \mbox{ else where } \end{cases} $$
If we set $\displaystyle \frac{2x}{1-x^2}=y, x^2y+2x-y=0\ \ \ \ (1)$
$\displaystyle\implies x=\frac{-1\pm\sqrt{1+y^2}}y$
Taking the '-' sign, $\displaystyle x=-\frac{\sqrt{1+y^2}+1}y,$ observe that either $\displaystyle x<-1$ or $\displaystyle x>1$
Taking the '+' sign, $\displaystyle x=\frac{\sqrt{1+y^2}-1}y=\frac y{\sqrt{1+y^2}+1},$ observe that $\displaystyle-1\le x\le 1$
One Observation:
If we set $\displaystyle x=\tan\phi, y=\frac{2x}{1-x^2}=\tan2\phi$
If $x_1,x_2$ be the two roots of $(1),$
$\displaystyle x_1\cdot x_2=\frac{-y}y=-1$ (assuming $y\ne0$) and $\displaystyle x_1+x_2=-\frac2y=-\frac2{\tan2\phi}=-2\cot2\phi$
$\displaystyle x_1=\tan\phi,x_2=-\frac1{x_1}=-\cot\phi$ and $\displaystyle x_1+x_2=\tan\phi-\cot\phi=-2\cdot\frac{1-\tan^2\phi}{2\tan\phi}=-\frac2{\tan2\phi}=-2\cot2\phi$