Starting from an odd number $n$, example analyzing the sequence for $\quad n=57$
$57\quad\rightarrow 172\rightarrow 86\rightarrow 43\rightarrow 130\rightarrow 65\rightarrow 196\rightarrow 98\rightarrow 49\rightarrow 148\rightarrow 74\rightarrow 37\rightarrow 112\rightarrow 56\rightarrow 28\rightarrow 14\rightarrow 7\rightarrow 22\rightarrow 11\rightarrow 34\rightarrow 17\rightarrow 52\rightarrow 26\rightarrow 13\rightarrow 40\rightarrow 20\rightarrow 10\rightarrow 5\rightarrow 16\rightarrow 8\rightarrow 4\rightarrow 2\rightarrow 1$
find the next odd elements of the sequence:
$n_o^1=43;\quad n_o^2=65;\quad n_o^3=49;\quad n_o^4=37;\quad n_o^5=7;\quad n_o^6=11;\quad n_o^7=17;\quad n_o^8=13;\quad n_o^9=5;\quad n_o^{10}=1$
we indicate with $k_o$ the number of odd elements and with $k_e$ the number of even elements of the sequence therefore:
$k_o=10$
$k_e=22$
We know that starting from an odd number it is possible to find the following odd numbers in the sequence using the following formula:
$n_o^1=\frac{3 \cdot n +1}{2^{a_1}}$
$n_o^2=\frac{3 \cdot n_o^1 +1}{2^{a_2}}$
$\cdots$
so in our example we have:
$n_o^1=43=\frac{3 \cdot 57 +1}{2^2}$
$\cdots$
$a_1=2;\quad a_2=1;\quad a_3=2;\quad a_4=2;\quad a_5=4;\quad a_6=1;\quad a_7=1;\quad a_8=2;\quad a_9=3;\quad a_{10}=4 $
and
$k_e=22=a_1+a_2+ \ldots +a_{10}$
From which it follows that in case the sequence reaches the number $1$ we have:
$$n = \frac{2^{k_e}-b}{3^{k_o}}\tag1$$
$$b = \sum_{i=0}^{k_o-2} {3^{i} \cdot 2^{\left(\sum_{j=1}^{k_o-1-i} {a_{j}}\right)}} \quad + \quad 3^{k_o-1} $$
applying $(1)$ to our example we have:
$57=\frac{2^{22}-828511}{3^{10}}$
$828511=2^{18}+3 \cdot 2^{15}+3^2 \cdot 2^{13}+3^3 \cdot 2^{12}+3^4 \cdot 2^{11}+3^5 \cdot 2^7+3^6 \cdot 2^5+3^7 \cdot 2^3+3^8 \cdot 2^2+3^9$
If we now set $\quad a_1=4 \quad$ we obtain $\quad n=229 \quad$
$229=\frac{2^{24}-3254995}{3^{10}}$
$3254995=2^{20}+3 \cdot 2^{17}+3^2 \cdot 2^{15}+3^3 \cdot 2^{14}+3^4 \cdot 2^{13}+3^5 \cdot 2^9+3^6 \cdot 2^7+3^7 \cdot 2^5+3^8 \cdot 2^4+3^9$
But if we set $\quad a1=3\quad$ we don't find any solution.
Is there a way to understand if given a combination $(a_1,a_2, \cdots ,a_m)$ you can find a number $n$ that has that sequence as a solution?
Edit
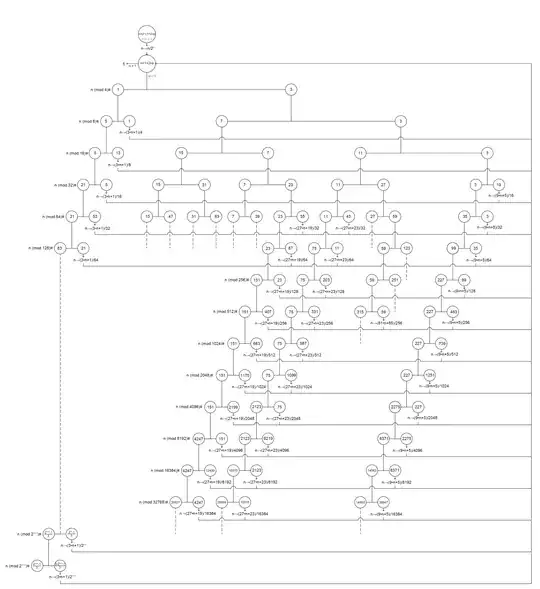
I thought that a sequence of odd numbers could be found (skipping some numbers of the original sequence) in such a way as to always obtain numbers lower than the previous one.
I started making this chart but already analyzing the number $27$ I encountered some difficulties.
Example:
considering the sequence of odd numbers $\quad 19 \rightarrow 29 \rightarrow 11 \quad$ can be directly simplified to $\quad 19 \rightarrow 11 \quad$
just as $ \quad 51 \rightarrow 77 \rightarrow 29 \quad$ can be simplified directly to $\quad 51 \rightarrow 29 \quad$
and then considering $\quad (9\cdot n +5)/16 \quad$ we have $ \quad (19+32\cdot k) \rightarrow (11 +18\cdot k) $
Note that in this case $a_1=1,\quad a_2=3 \quad$ and $\quad n_o^2 = \frac{3^{k_0}\cdot n+b}{2^{k_e}} \quad$with$\quad k_o=2,\quad k_e=4, \quad $and $\quad b=5$
For the numbers $\quad 3 \pmod {16 } \quad$ I think you can see a pattern like you can see in the graph.
Do you think you can complete the graph above?
Edit:
I haven't found a complete scheme for the graph yet but here OEIS A020914 I found an indication for the exponents to be used for the modulus $2^c$ then for $x\geq 0$ we have:
$n\rightarrow\frac{3 \cdot n+1}{2^{2 \cdot x+2}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{2^{2 \cdot x+2}-1} {3} \pmod {2^{2 \cdot x+3}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{3 \cdot n+1}{2^{2 \cdot x+3}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{5 \cdot 2^{2 \cdot x+3}-1}{3} \pmod {2^{2 \cdot x+4}}$
$$$$
$n\rightarrow \frac{9 \cdot n+5}{2^{6 \cdot x+4}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{11 \cdot 2^{6 \cdot x+4}-5} {9} \pmod {2^{6 \cdot x+5}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{9 \cdot n+5}{2^{6 \cdot x+5}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{ 2^{6 \cdot x+5}-5}{9} \pmod {2^{6 \cdot x+6}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{9\cdot n+5}{2^{6 \cdot x+6}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{5 \cdot2^{6\cdot x+6}-5} {9} \pmod {2^{6 \cdot x+7}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{9 \cdot n+5}{2^{6 \cdot x+7}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{7 \cdot 2^{6\cdot x+7}-5}{9} \pmod {2^{6 \cdot x+8}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{9 \cdot n+5}{2^{6 \cdot x+8}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{17 \cdot2^{6 \cdot x+8}-5} {9} \pmod {2^{6 \cdot x+9}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{9\cdot n+5}{2^{6 \cdot x+9}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{13 \cdot 2^{6 \cdot x+9}-5}{9} \pmod {2^{6 \cdot x+10}}$
$$$$ $n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+5}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{47 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+5}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+6}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27\cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+6}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{37 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+6}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+7}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+7}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{5 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+7}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+8}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27\cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+8}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{43 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+8}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+9}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27\cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+9}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{35 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+9}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+10}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+10}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{31 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+10}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+11}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+11}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{29 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+11}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+12}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+12}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{ 2^{18 \cdot x+12}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+13}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27\cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+13}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{41 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+13}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+14}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+14}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{7 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+14}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+15}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27\cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+15}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{17 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+15}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+16}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+16}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{49 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+16}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+17}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27\cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+17}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{11 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+17}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+18}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+18}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{19 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+18}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+19}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+19}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{23 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+19}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+20}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+20}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{25 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+20}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+21}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+21}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{53 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+21}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+22}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+19}{2^{18 \cdot x+22}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{13 \cdot 2^{18\cdot x+22}-19} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+23}}$ $$$$ $n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+23}{2^{18 \cdot x+5}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{37 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+5}-23} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+6}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{27 \cdot n+23}{2^{18 \cdot x+6}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{5 \cdot 2^{18 \cdot x+6}-23} {27} \pmod {2^{18 \cdot x+7}}$
$\cdots$ $$$$ $n\rightarrow \frac{81\cdot n+65}{2^{54 \cdot x+7}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{91 \cdot 2^{54 \cdot x+7}-65} {81} \pmod {2^{54 \cdot x+8}}$
$n\rightarrow \frac{81 \cdot n+65}{2^{54 \cdot x+8}} \quad $ if $\quad n \equiv \frac{5 \cdot 2^{54 \cdot x+8}-65} {81} \pmod {2^{54 \cdot x+9}}$
$\cdots$