$\huge{\text{Preliminaries}}$
This answer does not require a calculator, but assumes that we can add/subtract/multiply/divide numbers of up to five digits, and uses the following facts:
$3.1415<\pi<3.1416$
$1.414<\sqrt2<1.415$
$1.732<\sqrt3<1.733$
$\sqrt{5-2\sqrt5}<0.727$ which can be proved:
$\sqrt5>2.236$
$5-2\sqrt5<0.528$
$\sqrt{5-2\sqrt5}<\sqrt{0.528}<\sqrt{0.727^2}=0.727$
$\tan{\dfrac{\pi}{5}}=\sqrt{5-2\sqrt5}$ which is proved here.
$\huge{\text{Proof by contradiction: assume the answer is yes}.}$
$\huge{\text{Define $\alpha$ and $\beta$}.}$
Let radius $=1$.
Call the centre $O$.
$\alpha=\angle{AOB}$
$\beta=\angle{AOC}$

$\huge{\text{Show that }\alpha>2.1.}$
$2\times\text{Area}_{\text{minor segment }AB}=\alpha-\sin{\alpha}=\dfrac{2\pi}{5}$
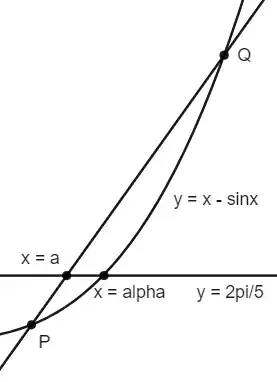
Between $P\left(\dfrac{2\pi}{3},\dfrac{2\pi}{3}-\dfrac{\sqrt3}{2}\right)$ and $Q\left(\dfrac{3\pi}{4},\dfrac{3\pi}{4}-\dfrac{\sqrt2}{2}\right)$, the curve $y=x-\sin{x}$ is concave up, so the curve lies to the right of line segment $PQ$.
We can show that $P$ is below $y=\dfrac{2\pi}{5}$, and $Q$ is above $y=\dfrac{2\pi}{5}$:
$\dfrac{2\pi}{3}-\dfrac{\sqrt3}{2}<\dfrac{2(3.15)}{3}-\dfrac{1.7}{2}=1.25<1.256=\dfrac{2(3.14)}{5}<\dfrac{2\pi}{5}$
$\dfrac{2\pi}{5}<\dfrac{2(3.2)}{5}=1.28<1.45=\dfrac{3(3)}{4}-0.8<\dfrac{3\pi}{4}-\dfrac{\sqrt2}{2}$
Let $a=$ x-coordinate of intersection of $y=\dfrac{2\pi}{5}$ and line segment $PQ$.
$\alpha >a=\dfrac{\frac{2\pi}{5}+\frac{9\sqrt3}{2}-4\sqrt2}{1+\frac{6}{\pi}(\sqrt3-\sqrt2)}>\dfrac{0.4(3.14)+4.5(1.732)-4(1.415)}{1+\frac{6}{3.14}(1.733-1.414)}=\dfrac{3.39}{\frac{5.054}{3.14}}>\dfrac{3.39}{1.61}>2.1$
$\huge{\text{Show that }\beta>2.82.}$
$2\times\text{Area}_{\text{segment }ADC}=\beta-\sin{\beta}=\dfrac{4\pi}{5}$
Between $R\left(\dfrac{5\pi}{6},\dfrac{5\pi}{6}-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)$ and $S\left(\pi,\pi\right)$, the curve the curve $y=x-\sin{x}$ is concave up, so the curve lies to the right of line segment $RS$.
We can show that $R$ is below $y=\dfrac{4\pi}{5}$, and $S$ is above $y=\dfrac{4\pi}{5}$:
$\dfrac{5\pi}{6}-\dfrac{1}{2}<\dfrac{5(3.6)}{6}-\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{4(3)}{5}<\dfrac{4\pi}{5}$
$\dfrac{4\pi}{5}<\pi$
Let $b=$ x-coordinate of intersection of $y=\dfrac{4\pi}{5}$ and line segment $RS$.
$\beta >b=\dfrac{\frac{4\pi}{5}+3}{1+\frac{3}{\pi}}>\dfrac{0.8(3.1415)+3}{1+\frac{3}{3.1415}}>\dfrac{5.5132}{1.955}>2.82$
$\huge{\text{Show that }\angle{BAC}<0.6816}.$
$\angle{BAC}=\dfrac{1}{2}{\angle{BOC}}=\dfrac{1}{2}{\left(2\pi-\alpha-\beta\right)}<\dfrac{1}{2}(2(3.1416)-2.1-2.82)=0.6816$
$\huge{\text{Show that }\alpha<2.12.}$
$2\times\text{Area}_{\text{minor segment }AB}=\alpha-\sin{\alpha}=\dfrac{2\pi}{5}$

Between $(0,0)$ and $(\pi,\pi)$, the curve $y=x-\sin{x}$ is concave up, so the curve lies to the left of the tangent to the curve at $x=\dfrac{2\pi}{3}$.
Let $c=$ x-coordinate of intersection of $y=\dfrac{2\pi}{5}$ and the tangent to the curve at $x=\dfrac{2\pi}{3}$.
$\alpha<c=\dfrac{\sqrt3}{3}+\dfrac{22\pi}{45}<\dfrac{1.74}{3}+\dfrac{22(3.15)}{45}=2.12$
$\huge{\text{Show that }5-5\cos{\alpha}<7.62.}$

For $\dfrac{\pi}{2}<x<\pi$, the curve $y=5-5\cos{x}$ is concave down, so the curve lies below the tangent to the curve at $x=\dfrac{2\pi}{3}$, which has equation $y=\dfrac{5\sqrt3}{2}\left(x-\dfrac{2\pi}{3}\right)+7.5$.
$5-5\cos{\alpha}<5-5\cos{2.12}<\dfrac{5\sqrt3}{2}\left(2.12-\dfrac{2\pi}{3}\right)+7.5<5.3(1.733)-\dfrac{5(3.141)(1.732)}{3}+7.5<7.62$
$\huge{\text{Show that }\angle{BAC}>0.6817}.$
In the diagram of the circle and chords, $\text{Area}_{\text{triangle}}=\dfrac{\pi}{5}\text{ and }AB=2\sin{\dfrac{\alpha}{2}}\implies\angle{BAC}=\arctan{\left(\dfrac{2\pi}{5-5\cos{\alpha}}\right)}$
$\angle{BAC}=\arctan{\left(\dfrac{2\pi}{5-5\cos{\alpha}}\right)} > \arctan{\left(\dfrac{2\pi}{7.62}\right)}>\arctan{\left(\dfrac{2(3.14)}{7.62}\right)}>\arctan{0.82}$

Between $T\left(\sqrt{5-2\sqrt5}, \dfrac{\pi}{5}\right)$ and $U\left(1, \dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)$, the curve $y=\arctan{x}$ is concave down, so the curve lies above line segment $TU$, which has equation $y=\dfrac{\frac{\pi}{20}}{\sqrt{5-2\sqrt5}-1}(1-x)+\dfrac{\pi}{4}$.
$\angle{BAC}>\arctan{0.82}>\dfrac{\frac{\pi}{20}}{\sqrt{5-2\sqrt5}-1}(1-0.82)+\dfrac{\pi}{4}>\dfrac{\frac{3.141}{20}}{0.727-1}(0.18)+\dfrac{3.141}{4}>0.6817$
$\huge{\text{Contradiction}}.$
$\huge{\text{Therefore the answer is no}}.$






