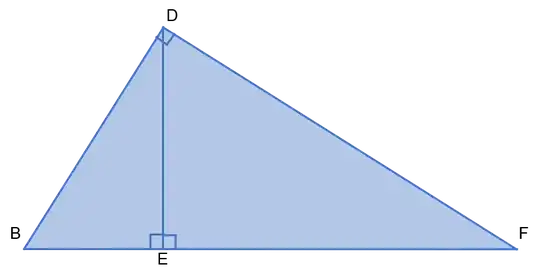
-
Given image:
- $\triangle\mathit{BDE}$ is an altitude right triangle as given by the image.
- $\triangle\mathit{BDE}$ and $\triangle\mathit{FDE}$ both contain 90° given by the image; therefore, $\triangle\mathit{BDE}$ and $\triangle{\mathit{FDE}}$ are both right triangles.
- $\triangle\mathit{BDE}$ is an altitude right triangle with $\triangle\mathit{FDE}$ as given by the image; therefore, $\triangle\mathit{BDE}\sim\triangle\mathit{FDE}$
- If $\triangle\mathit{BDE}$ is similar to $\triangle\mathit{FDE}$ then:
- If these triangles are similar, then the ratio of each of the sides of $\triangle\mathit{BDE}$ to the corresponding sides of $\triangle\mathit{FDE}$ is common; therefore, the equations below can be derived:
- $\overline{\mathit{DE}}^{2}=\overline{\mathit{BE}}\overline{\mathit{EF}}$
- $\overline{\mathit{DF}}^{2}=\overline{\mathit{EF}}\overline{\mathit{BF}}$
- $\overline{\mathit{BE}}+\overline{\mathit{EF}}=\overline{\mathit{BF}}$ as given by the image
- Given these equations algebra can then be performed to solve for $\overline{\mathit{DF}}$. Algebra:
- Rearranging:$\overline{\mathit{DE}}^{2}=\overline{\mathit{BE}}\overline{\mathit{EF}}$ to get $\frac{\overline{\mathit{DE}}^{2}}{\overline{\mathit{EF}}}=\overline{\mathit{BF}}.$
- $\overline{\mathit{DF}}^{2}=\overline{\mathit{EF}}\overline{\mathit{BF}}$
- Substituting:$$\overline{\mathit{DF}}^{2}=\overline{\mathit{EF}}(\overline{\mathit{BE}}+\overline{\mathit{EF}})$$
- Substituting Again:$$\overline{\mathit{DF}}^{2}=\overline{\mathit{EF}}(\frac{\overline{\mathit{DE}}^{2}}{\overline{\mathit{EF}}} + \overline{\mathit{EF}})$$
- Simplifying:$$\overline{\mathit{DF}}^{2}=\overline{\mathit{DE}}^{2}+\overline{\mathit{EF}}^{2}$$
Is this proof general enough to be used as a general proof?