An ellipse is the geometric place of the points $P(x,\,y)$ of the plane for which the sum $d > 0$ of the distances from two fixed points $F_1(x_1,\,y_1),\,F_2(x_2,\,y_2)$, called foci, remains constant:
$$
\sqrt{(x-x_1)^2+(y-y_1)^2} + \sqrt{(x-x_2)^2+(y-y_2)^2} = d\,.
$$
Manipulating this equation we obtain the Cartesian equation of the desired ellipse.
Algorithmically, given two points $F_1(x_1,\,y_1),\,F_2(x_2,\,y_2)$ and a number $d > 0$, if:
$$
\Delta := d^2 - (x_1-x_2)^2 - (y_1-y_2)^2 > 0
$$
then an ellipse of parametric equations was identified:
$$
(x,\,y) = (A + B\,\cos\theta + C\,\sin\theta, \; D + E\,\cos\theta + F\,\sin\theta)\,, \; \; \; \text{with} \; \theta \in [0,\,2\pi)
$$
where:
$$
\begin{aligned}
& A = \frac{x_1 + x_2}{2}\,, \; \; \;
B = \frac{\sqrt{\Delta + \left(x_1-x_2\right)^2}}{2}\,, \; \; \; \; \;
C = 0\,, \\
& D = \frac{y_1 + y_2}{2}\,, \; \; \;
E = \frac{\left(x_1-x_2\right)\left(y_1-y_2\right)}{4\,B}\,, \; \; \;
F = \frac{d\,\sqrt{\Delta}}{4\,B}\,.
\end{aligned}
$$
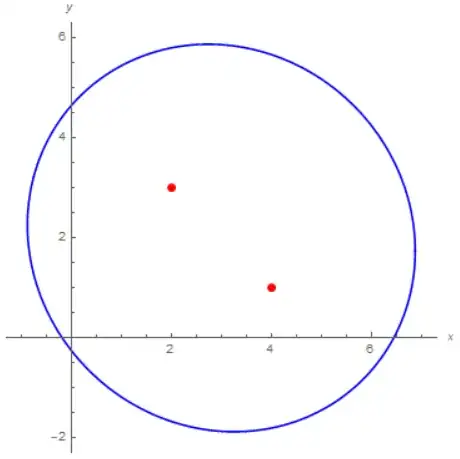
Specifically, being $(x_1,\,y_1)=(2,\,3)$, $(x_2,\,y_2)=(4,\,1)$ and $d = 8$:
- Cartesian equation: $15\,x^2 + 15\,y^2 + 2\,x\,y - 94\,x - 66\,y - 17 = 0$;
- parametric equations: $x = 3+\sqrt{15}\,\cos\theta, \; y = 2 - \frac{\sqrt{15}}{15}\,\cos\theta - \frac{4\sqrt{210}}{15}\,\sin\theta$, with $0 \le \theta < 2\pi$.