Let me first rephrase the problem a little bit
$$
P(\theta)d\theta = \left[\int_{0}^1 dy P(\max\{X_i\}=y)\cdot P\left(\bar{X}=\frac{y}{n\theta} \middle| \max \{X_i\}=y \right)\right]d\bar{X}
$$
It is mentioned in this link that
$$
P(\max\{X_i\}=y)=y^n
$$
Without losing generosity, I can also reorder the ${X_i}$ to be ${\mu_i}$,so that $\mu_n=\max\{X_i\}=y$.
Now I can define $\bar{\mu}=\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}\mu_i/(n-1)$ , thus
$$
P\left(\bar{X}=\frac{y}{n\theta} \middle| \max \{X_i\}=y \right)d\bar{X} = P\left(\bar{\mu}=\frac{1-\theta}{(n-1)\theta}y \middle| \mu_i \sim Unif(0,y)\right)d\bar{\mu}
$$
Further define $z_i=y\mu_i$, we can write
$$
P(\theta)d\theta = \int_{0}^1 dy d\bar{\mu} \left[ y^n\cdot P\left(\bar{\mu}=\frac{1-\theta}{(n-1)\theta}y \middle| \mu_i \sim Unif(0,y) \right)\right] \\
= \int_{0}^1 dy \underbrace{ d\bar{z} \left[P\left(\bar{z}=\frac{1-\theta}{(n-1)\theta}y \middle| z_i \sim Unif(0,1) \right)\right] }_{P_0}
$$
Notice the part I labeled as $P_0$ is independent of $y$, so we can carry out the integral trivially.
$$
P(\theta)d\theta = P_0= \left[P\left(\bar{z}=\frac{1-\theta}{(n-1)\theta}y \middle| z_i \sim Unif(0,1) \right)\right] d\bar{z} \\
=\left[P\left(\bar{z}=\frac{1-\theta}{(n-1)\theta}y \middle| z_i \sim Unif(0,1) \right)\right] \left|\frac{1}{(n-1)\theta^2}\right|d\theta
$$
I believe there is some general analytic form for this distribution of $\bar{z}$ for arbitrary $n$, but I just can't solve that. However, there are some solvable examples to test this formula:
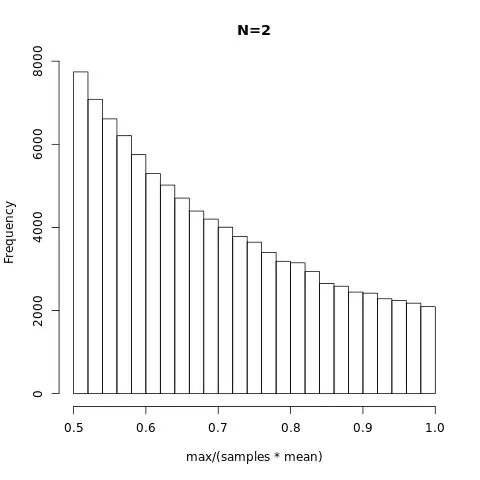
n=2:
$$
P(\theta)=\left[P\left(z_1=\frac{1-\theta}{\theta} \middle| z_1 \sim Unif(0,1) \right)\right] \frac{1}{\theta^2} = \frac{1}{\theta^2}
$$

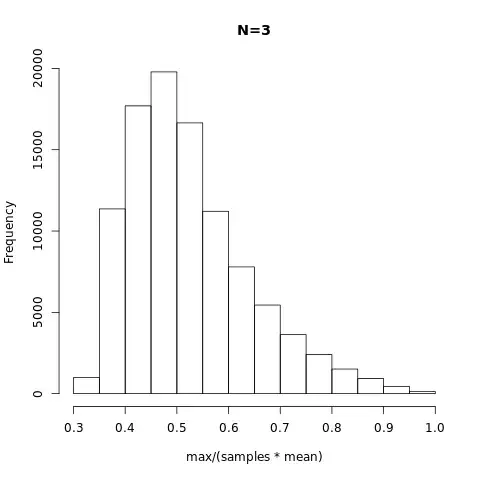
n=3:
$$
P(\theta)=\left[P\left(\frac{z_1+z_2}{2}=\frac{1-\theta}{2\theta} \middle| z_1,z_2 \sim Unif(0,1) \right)\right] \frac{1}{2\theta^2} =\left[2-4*\left|\frac{1-\theta}{2\theta}-0.5\right|\right] \frac{1}{2\theta^2}
$$
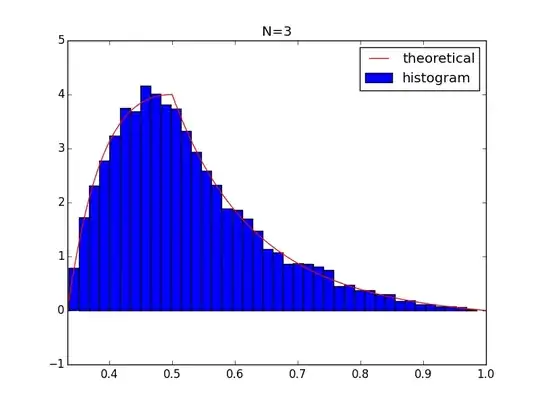
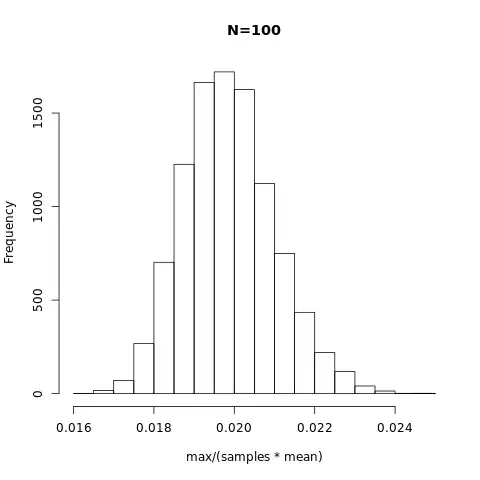
n is large
When $n$ is large, from central limit theorem, we know that
$$
P\left(\bar{z}=\frac{1-\theta}{(n-1)\theta} \middle| z_i \sim Unif(0,1) \right) \approx P_\text{Gauss}\left(\frac{1-\theta}{(n-1)\theta}, \mu=0.5, \sigma^2=\frac{1}{12n}\right)\\
=\sqrt{\frac{6n}{\pi}}\exp\left[-6n\left(\frac{1-\theta}{(n-1)\theta}-0.5\right)^2\right]
$$
With some approximation $n\gg 1$, we can write down the form more neatly as
$$
\lim_{n\to \infty}P(\theta)\approx \frac{1}{n\theta^2} \sqrt{\frac{6n}{\pi}}\exp\left[-6n\left(\frac{1-\theta}{n\theta}-0.5\right)^2\right]
$$
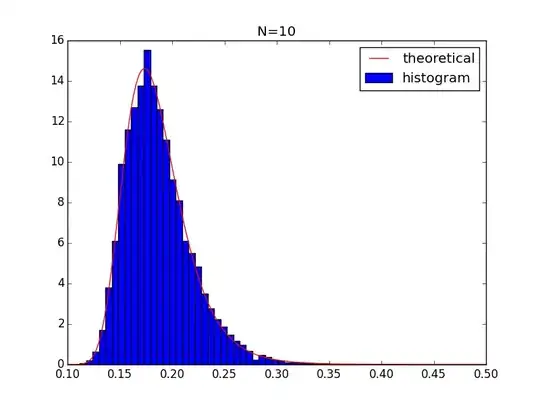
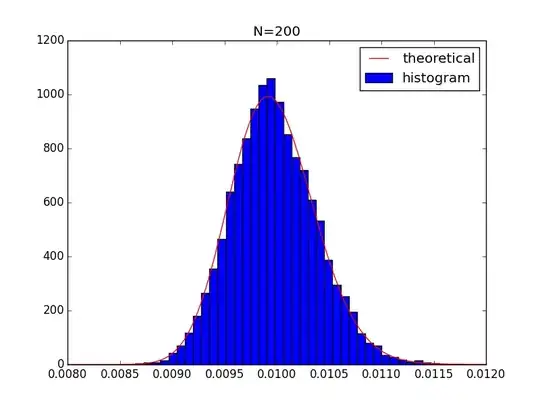
MLE with large n
The value of maximum probability density is approximately
$$
\frac{1-\theta}{n\theta}=0.5 \Rightarrow \theta=\frac{2}{n}
$$