We will need the joint comulatice distribution function $F_{Y_1,Y_2}(u,v)=P(Y_1<u,Y_2<v).$
Now,
$$P(Y_1<u,Y_2<v)=P(Y_1<u,Y_2<v, X_1\le X_2)+P(Y_1<u,Y_2<v ,X_2<X_1)=$$
$$=P(X_1<u,X_2<v, X_1\le X_2)+P(X_2<u,X_1<v ,X_2<X_1).$$
First,
$$P(X_1<u,X_2<v, X_1\le X_2)=
\begin{cases}
-\frac{u^2}{2}+uv,&\text{ if }& 0\le u\le v \le 1\\
\frac{v^2}{2},&\text{ if }& 0\le v<u \le1
\end{cases}.$$
The figure below explains how I calculated the two pieces of surface area:
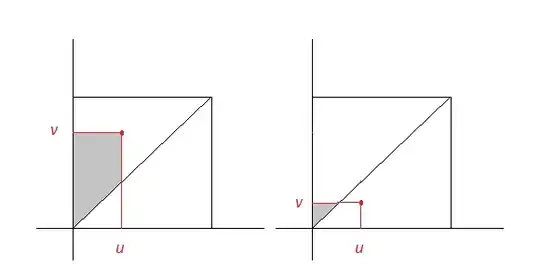
Second,
$$P(X_2<u,X_1<v ,X_2<X_1)=P(X_2<u,X_1<v, X_2\le X_1)=
\begin{cases}
-\frac{u^2}{2}+uv
,&\text{ if }& 0\le u\le v \le 1\\
\frac{v^2}{2},&\text{ if }& 0\le v<u \le1
\end{cases}.$$
(A figure similar to the one above would explain the latter result.)
We can calculate the joint cdf:
$$F_{Y_1,Y_2}(u,v)=$$$$=P(X_1<u,X_2<v, X_1\le X_2)+P(X_2<u,X_1<v ,X_2<X_1)=$$
$$=\begin{cases}
-u^2+2uv,&\text{ if }& 0\le u\le v \le 1\\
v^2,&\text{ if }& 0\le v<u \le1
\end{cases}.$$
The joint pdf can be calculated the following way:
$$f_{Y_1,Y_2}(u,v)=\frac{{\partial} ^2}{\partial u \partial v}F_{Y_1,Y_2}(u,v)=\begin{cases}
2,&\text{ if }& 0\le u\le v \le 1\\
0,&\text{ otherwise. }
\end{cases}$$
Then we will need the following marginal density:
$$f_{Y_2}(v)=\int_0^vf_{Y_1,Y_2}(u,v)du=2\int_0^v\ du=2v;\ 0\le v\le 1.$$
To answer the first question: By definition
$$f_{Y_1 \mid Y_2=v}(u)=\frac{f_{Y_1,Y_2}(u,v)}{f_{Y_2}(v)}=\begin{cases}
\frac{1}{v},&\text{ if }& 0\le u\le v \le 1\\
0,&\text{ else. }
\end{cases} \tag 1$$
To answer the second question: First let's calculate the cdf of $Y_2-Y_1$. By definition
$$F_{Y_2-Y_1}(x)=P(Y_2-Y_1<x)=E[P(Y_2-Y_1<x \mid Y_2)]. $$
Then
$$P(Y_2-Y_1<x \mid Y_2=v)=
\begin{cases}
0,&\text{ if } x<0\\
P(Y_1>v-x\mid Y_2=v),& \text{ if } 0\le x \le v \le 1\\
1,&\text{ if } x>v
\end{cases}$$
where $0\le v \le 1$.
Considering $(1)$ we have for $0\le x \le v \le 1$
$$P(Y_1>v-x\mid Y_2=v)=\frac 1v\int_{v-x}^v\ du=\frac xv.$$
So, for a given $0\le x \le 1$
$$P(Y_2-Y_1<x \mid Y_2=v)=\begin{cases}
1,& \text{ if } 0\le v\le x\\
\frac xv,&\text{ if } x\le v\le 1.\\
\end{cases}$$
As a result, for $0\le x \le 1$
$$F_{Y_2-Y_1}(x)=\int_0^1P(Y_2-Y_1<x \mid Y_2=v)f_{Y_2}(v)\ dv=$$
$$=2\int_0^x v \ dv + 2x\int_x^1 \ dv=2x-x^2.$$
Finally, $$f_{Y_2-Y_1}(x)=\begin{cases}
2-2x,& \text{ if } 0\le x \le 1 \\
0,&\text{ otherwise. }
\end{cases}$$
