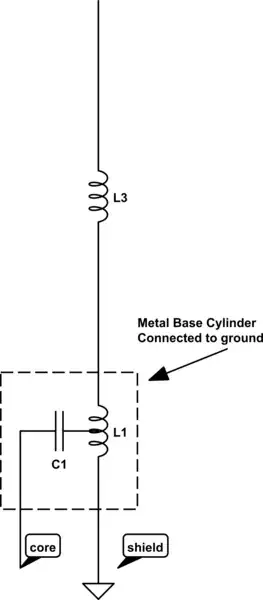
This is the insides of a common dual band antenna 2m/70cm, made by diamond or nagoya. its generally labelled as: 1/2 wave radialless (144MHz), 2 x 5/8 wave radialless (430MHz) Its meant to be ground independant.
Im trying to find the design name for the tuning/matching circuit at the bottom and how it works.
- For example what stops the signal going down to ground at L1 rater than going up the elements ?
- Does the coil below the C1 tap point provide the counterpoise/ground for the antenna, and the part of coil above act as matching/loading coil for lower element ?
- calculators/plans around for this type or antenna ?
- generally how does it work, im also trying to model it such as in 4nec2
simulate this circuit – Schematic created using CircuitLab