Is AES GCM without GMAC vulnerable against bit-flip attacks? Let's assume the plaintext is known for some reason (e.g. it can be guessed). In my opinion, I can flip bits in the ciphered blocks and can so generate a plaintext, which is flipped at the same position. So it would be easy to change 0x01 to 0x00 in the plaintext, even when I don't know the key or Initialization vector.
-
1Do you mean "Lets assume the plaintext is known"? – Martin Thompson Feb 07 '22 at 14:15
-
1HMAC ensures integrity, without it there is no way for the receiver to check that the ciphertext wasn't tampered with. Therefore, a number of attacks apply and in particular simple bitflips. – Marc Ilunga Feb 07 '22 at 14:19
-
Sorry, I mean "Lets assume the plaintext is known" – MichaelW Feb 07 '22 at 14:24
-
I talk about GMAC, not HMAC. – MichaelW Feb 07 '22 at 14:25
-
3As far as I understand, GCM mode is defined to include the authentication code - from the spec "The two functions that comprise GCM are called authenticated encryption and authenticated decryption"... so without the GMAC, it is potentially vulnerable to all kinds of attacks. But you're not supposed to do that :) – Martin Thompson Feb 07 '22 at 14:27
-
I work for a real world project. There it can be chosen to use just encryption (GCM) or encryption + authentication (GCM/GMAC). There was a discussion to use GCM without GMAC, but I think for the reasons above this is quite dangerous. – MichaelW Feb 07 '22 at 14:30
-
1Seems my autocorrect prefers HMAC to GMAC. Anyway, the statement should still hold. An addition could be that without GMAC, we fallback on CTR. – Marc Ilunga Feb 07 '22 at 14:34
-
1If they are discussing 'lets do GCM without passing or validating the tag', they're effectively saying 'lets use a broken version of GCM'. If they don't/can't spend the bandwidth to send the GCM tag, they shouldn't be using GCM at all. – poncho Feb 07 '22 at 15:47
1 Answers
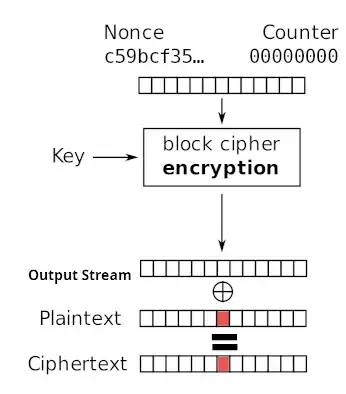
As an Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data, AES-GCM internally uses CTR mode and GCM adds authentication and integrity. Without GCM one can have only Ind-CPA security.
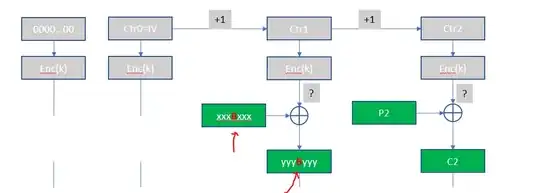
CTR in AES-GCM starts IV incremented ($inc_{32}(J_0)$ in NIST format and if IV size is not 96-bit then the IV is processed). The initial $J_0$ is used in the authentication tag calculation.
The rest is the usual CTR mode. If one knows the message, they can change the message into whatever message they want. Just x-or (the bit-flip attack) the necessary bits.
Consider the encryption. One has no control of the output stream. On the other hand, if the ciphertext is modified, only the plaintext is changed. Or see in the equation;
$$C_i = O_i \oplus P_i$$ The output stream $O_i$ is fixed by the block cipher encryption therefore changing the $C_i$ modifies the $P_i$.
This is, however, is not a known-plaintext attack! In a known-plaintext attack, one has known-plaintext pairs and tries to determine the key. CTR mode is secure against KPA attacks and actually, that is a lesser attack than Ind-CPA.
- 48,443
- 11
- 116
- 196
-
Ah... and what kind of attack would be the bit-flipping which modifies a known plaintext by flipping bits in the ciphertext? Or isn't this an attack, because it is trivial? – MichaelW Feb 07 '22 at 17:55
-
1In general terms, it is an active attack that modifies the ciphertext. In specific, it is a bit-flipping attack even CBC mode has bit flipping attack – kelalaka Feb 07 '22 at 17:59
-
But anyway, in practical terms I can state, that GCM without GMAC is not secure when the plain text can be guessed? Right? – MichaelW Feb 07 '22 at 18:02
-
Remember, the main target of attackers in the encryption is accessing the message which doesn't mean that one has reached the key with brute force or other means. In general, it is revealed with the key. In your case, once you reveal the message, now you have a known-plaintext pair to attack with at least KPA. Remember CTR mode Ind-CPA secure. – kelalaka Feb 07 '22 at 18:18
-
1Guessing the message makes the attack easier in the case if the IV-reuse under the same key. This will reveal the other message not the key. – kelalaka Feb 07 '22 at 18:19
-
Lets say there is a command to be transmitted to a power plant, which can be "Set Status=0" and "set Status=1". If Mallory in the middle can guess that the first command is transmitted, he can, just by bit-flipping, change 0 to 1 without knowing the key and without re-using the IV. If "1" means for instance "switch off power plant", Mallory can easily cause big harm. However, when the command is additionally protected by authentication tag and each IV is used only once, this scenario cannot happen. This is a simple version of my real world problem. Do you think my fears are realistic? – MichaelW Feb 07 '22 at 18:37
-
1The games we played in the Ind-CPA, Ind-CCAx we talk about a single bit with multiple tries of the adversary. We expect that the advantage of the adversary is $1/2+\epsilon$ where $\epsilon$ is a negligible amount. So the adversary has only a negligible chance of success. – kelalaka Feb 07 '22 at 19:01